Right ventricle
Right ventricle – the camera of heart of the person in which the small circle of blood circulation begins. In total cameras in heart four. A venous blood comes to a right ventricle from the right auricle at the time of a diastole via the three-leaved valve and is pumped over at the time of a systole via the pulmonary valve in a pulmonary trunk.
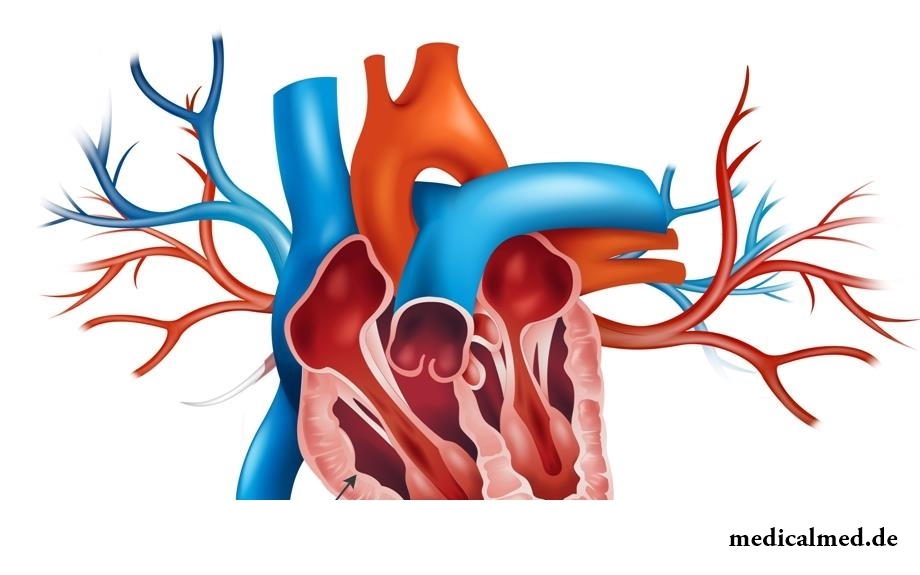
Structure of a right ventricle
The right ventricle is limited from left by back and front interventricular furrows on the surface of heart. It is separated from the right auricle by means of a coronal furrow. The outer edge of a ventricle has the pointed form and is called the right edge. In a form the ventricle reminds the wrong trihedral pyramid, with the basis directed up and to the right, and top – to the left and down.
The back wall of a ventricle has the flat form, and a lobby – convex. The internal left wall is an interventricular partition, it has the convex form (it is convex towards a right ventricle).
If to look at a right ventricle in a section at the level of a heart top, it is similar to the crack extended in the perednezadny direction. And if to look on border of an average and upper third of heart – that he reminds a form of a triangle which basis the partition between ventricles pressing in a cavity of right forms.
In a cavity of a ventricle there are two departments: back wide and front narrower. The front department is called an arterial cone, it has an opening by means of which connects to a pulmonary trunk. The back department is reported with the right auricle by means of the right atrioventricular opening.
On an internal surface of back department is available many moderator bands forming dense network.
On a circle of an atrioventricular opening the right atrioventricular valve which does not set in motion to the return blood flow from a ventricle to the area of the right auricle fastens.
The valve is formed by three triangular shutters: front, back and septal. All shutters act as free edges in a ventricle cavity.
The septal shutter is located closer to a partition of ventricles and fastens to a medial part of an atrioventricular opening. The front shutter fastens to a front part of a medial opening, it is turned towards an arterial cone. The back shutter is attached to a posteroexternal part of a medial opening. Often between back and septal shutters it is possible to see a small additional tooth.
The opening of a pulmonary trunk is located at the left and in front and conducts in a pulmonary trunk. At the edges of an opening it is possible to see three gates: front, left and right. Their free edges act in a pulmonary trunk and everything together they form the valve of a pulmonary trunk.
The diseases connected with a right ventricle
The following diseases of a right ventricle are most widespread:
- Stenosis of a pulmonary trunk;
- Hypertrophy of a right ventricle;
- Heart attack of a right ventricle;
- Blockade of a right ventricle.
Stenosis of a pulmonary trunk
The stenosis represents the isolated narrowing of a pulmonary artery. Narrowing of an exit in a pulmonary artery can be located at various levels:
- The subvalvular stenosis of a pulmonary artery is formed as a result of growth of fibrous and muscular tissue in infundibulyarny department of a ventricle.
- The stenosis of a fibrous ring is formed in the place of transition of a myocardium of a right ventricle to a pulmonary trunk.
- The isolated valve stenosis is the most often met heart pathology (about 9% of inborn heart diseases). At this defect the valve of a pulmonary artery represents a diaphragm with an opening, on diameter of equal from 2 to 10 mm. Division into shutters often is absent, commissures are maleficiated.
At a stenosis of a pulmonary trunk pressure in a right ventricle increases that increases load of it. As a result it leads to increase in a right ventricle.
Hypertrophy of a right ventricle
In fact, the hypertrophy of a right ventricle is not a disease, it is rather a syndrome which indicates increase in a myocardium and becomes the reason of a number of serious diseases.
Increase in a right ventricle is connected with growth of kardiomitotsit. As a rule, this state is pathology and is combined with other cardiovascular diseases.
Increase in a right ventricle meets quite seldom and is often diagnosed for patients with such diseases as pneumonia and chronic bronchitis, a pneumosclerosis and emphysema, a pneumosclerosis, bronchial asthma. As it was already written above, the stenosis or inborn heart disease can cause a hypertrophy of a right ventricle.
The mass of a right ventricle in a normality is approximately three times less than the mass of left. Dominance in healthy heart of electric activity of a left ventricle is connected with it. On this background it is much more difficult to reveal a hypertrophy of a right ventricle on the electrocardiogram.
Proceeding from extent of increase in a right ventricle, allocate the following types of a hypertrophy:
- Sharply expressed hypertrophy – when on weight a right ventricle exceeds left;
- The average hypertrophy – a left ventricle is more right, however in right the excitement processes connected with its increase are observed;
- Moderate hypertrophy – a left ventricle on weight much more right though right it is a little increased.
Heart attack of a right ventricle
Approximately at 30% of patients with the lower heart attack the right ventricle in a varying degree is surprised. The isolated heart attack of a right ventricle arises much less often. Often extensive heart attack leads to heavy right ventricular insufficiency at which Kussmaul's symptom, swelling of cervical veins, a hepatomegalia is observed. Arterial hypotonia is possible. In the first days raising of a segment of ST in additional chest assignments is often observed.
Extent of defeat of a right ventricle can be revealed by means of an ekhokardiogramma.
Blockade of a right ventricle
Blockade of a right ventricle occurs approximately at 0,6-0,4% of healthy people. The forecast of this disease depends on heart diseases. For example, at the isolated blockade the forecast quite favorable as there is no tendency to development of coronary heart disease.
Blockade of a right ventricle can develop as a result of an embolism of a pulmonary artery or a front heart attack. If blockade results from a heart attack, the negative outlook as in the first months often there comes heart failure and sudden death.
The blockade resulting from an embolism of a pulmonary artery usually tranzitorny is also observed preferential at patients with a disease of a pulmonary artery in a severe form.
The 74-year-old resident of Australia James Harrison became blood donor about 1000 times. It has a rare blood group which antibodies help to survive the newborn with a severe form of anemia. Thus, the Australian saved about two million children.

Women quite often suffer from complexes concerning the sizes of the bust. Strangely enough, reason душевног...
Section: Articles about health
Run - one of the most available and effective ways to revitalize the organism. Knowing about its extraordinary advantage, each of us at least once tried to make jogs, but only the few made these occupations regular. In spite of the fact that in jogging (easy an ozdor...
Section: Articles about health
The sclera and mucous membrane of an eye are intensively supplied with blood vessels which problem - to saturate nervous tissues of body with nutrients and oxygen. In a normality vessels are almost not noticeable, however at their expansion (owing to thinning of walls) become visible, painting a sclera in red color. Quite often red eyes - the signal of any trouble in an organism caused as external irritants, allergens, and diseases which need in about...
Section: Articles about health
Many parents of children at the age of 2-4 years face excessively whimsical behavior of the child. The kid exhausts constant crying...
Section: Slideshow
Feeding by a breast - the integral part of ideal motherhood allowing to come into contact with the kid and to create to it healthy immunity since early years. Nevertheless, this important process in life of mother and child can be saddened laktostazy − by a delay of milts...
Section: Articles about health
People know that thermal sources have salutary force long ago. Treatment by natural waters is one of the most ancient methods of disposal of the most different diseases. Bathtubs, souls, wrappings and inhalations, in combination with water reception inside help to improve a condition of the patients suffering from disturbances of work of a musculoskeletal system, bodies of digestive tract, cardiovascular, nervous, respiratory and secretory system, skin and endocrine п...
Section: Articles about health
Stroke (acute disorder of cerebral circulation) – one of the most widespread neurologic diseases. Annually in the world...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person in many respects depends on food. The organism will well function if during food it receive only useful substances, necessary vitamins and microelements. In this case there will be no problems with digestion, with лишн...
Section: Articles about health
Life activity of one-celled fungi of the sort Candida, related to yeast is a proximate cause of development of candidiasis (milkwoman). Normal these microorganisms are a part of the microflora living in an oral cavity and intestines of most of people and also in a female genital tract. The pathological phenomena are observed when fungi begin to breed too violently. At the same time there is an inflammatory process affecting mucous membranes and which is shown very nepr...
Section: Articles about health
Such trouble as the milkwoman's attack, at least once in life happened almost to each woman. Prevalence забол...
Section: Articles about health
Herpes simplex of the first type (the infectious disease which is shown periodic bubble rashes on lips is called) – one of the most widespread illnesses. Statistically, only 5% of inhabitants of our planet are unreceptive to its activator, and...
Section: Articles about health
Aging — natural and inevitable process. Over time our skin loses elasticity, on it saggings are formed, the face form loses former clearness. The procedure of nitevy lifting (nitevy tightening) can successfully solve this problem. In order that it is better to get acquainted with this popular procedure, we will tell you 6 cognitive facts about it....
Section: Articles about health
The person, as well as all other beings living on our planet feels weather changing. It is normal meteosensitivity, not...
Section: Articles about health
All are familiar with cold, and practically everyone believes that he has sufficient knowledge and experience that correctly to treat it. In practice most of people makes mistakes in attempts to get rid of rhinitis, and divides numerous delusions it....
Section: Articles about health
Season of activity of viral infections in the heat. Everyone can get sick, but probability of this unpleasant event it is possible and it is necessary to minimize. There is a number of rules, following to which will help or to avoid absolutely infection with flu or a SARS, or to have an illness benign and without essential complications. About ways of prevention of seasonal infections the speech in this article will also go....
Section: Articles about health
For the city dweller the fitness is the most convenient sport. It is enough to acquire the subscription to the gym to receive to a toast...
Section: Articles about health
All diseases from nerves – in this joke a big element of truth, are said by doctors. Constant stresses lead to decrease in protective forces of an organism, and it becomes vulnerable for a set of diseases. It is wrong to think that the stress is a problem of the present. Life of people and hundred...
Section: Articles about health
Diseases of joints often begin imperceptibly for the person. The first stages of destruction of the cartilaginous tissue providing soft and free sliding of heads of bones in joint bags proceed slowly and absolutely without serious consequences. Especially unpleasantly for the fact that this process is not connected with advanced age: degradation of joint surfaces is, as a rule, noticeable after 30 years. It means that practically each able-bodied person at any time can face sad results...
Section: Articles about health
Ability of an organism to resist to adverse environmental factors (to impact of temperature drops, humidity and pressure...
Section: Articles about health
Not without reason doctors say that 90% of diseases begin or develop because of misoperation of intestines. Disturbance of its functions is connected with various factors among which the important place belongs to excessive "clutter" of an intestinal path. In an organism скаплив...
Section: Articles about health
When overcomes feeling of hunger, and an opportunity to have dinner fully is absent, having a snack − the meals, small on volume, stabilizing sugar level in blood comes to the rescue. The relation of nutritionists to having a snack more often negative, but only because as snack people choose the most caloric products with the increased amount of "bystry" carbohydrates: cookies, rolls, chips, candies. Nevertheless, the advantage of having a snack is obvious to weight loss: the person avoids strong feeling of hunger...
Section: Articles about health
Maternal milk is the best food for the newborn. It is the unique natural product containing optimum set...
Section: Articles about health
Practically each person is familiar with the annoying, pulling, unscrewing pains caused by overcooling of muscles of a back. In certain cases inflammatory process is not limited to discomfort, being followed by emergence of hypostasis, consolidations, increase температ...
Section: Articles about health
Cold, puffiness of a nose, itch, the watering eyes - characteristic symptoms of the allergic rhinitis resulting from hit of allergens (pollen, house dust, hair of animals, etc.) on a mucous membrane of a nose. Unpleasant feelings often give trouble, serving as the reason of a headache, an acrimony, sleep disorders, and in certain cases and the states close to a depression. How to get rid of undesirable satellites of a disease if near at hand there are no antiallergic...
Section: Articles about health
Bathing in broths of medical flowers and plants (phytobathtub) was eurysynusic since Cleopatra who is a good judge of everything...
Section: Articles about health
Mushrooms - the surprising inhabitants of our planet having a set of wonderful qualities. Thanks to one of them, a mold mushroom of Penicillium notatum, the first natural antibiotic - penicillin was received nearly 80 years ago. The mankind is obliged to this opening миллио...
Section: Articles about health
In consciousness of our many compatriots idea that folk remedies if are no more effective, than medicinal "chemistry" strongly took roots, then are precisely less harmful. Unfortunately, it is not always fair: some methods of treatment consecrated with "century national experience" can work so on the patient that it will need urgent intervention of physicians....
Section: Articles about health