Streptomycin
Application instruction:
Streptomycin – the aminoglikozidny antibacterial drug used for treatment of tuberculosis and some other diseases.
Pharmacological effect of Streptomycin
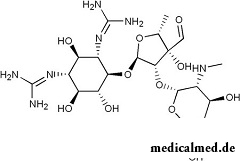 Active component of Streptomycin which is formed of radiant mushrooms of Streptomyces globisporus has bacteriostatic action.
Active component of Streptomycin which is formed of radiant mushrooms of Streptomyces globisporus has bacteriostatic action.
The antibiotic Streptomycin possesses a broad spectrum of activity, in particular, it is active in the relation:
- Streptococcus spp., including Enterococcus spp. and Streptococcus pneumoniae;
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- Some gram-positive microorganisms, including Staphylococcus spp.;
- Majority of gram-negative bacteria: Yersinia pestis, Salmonella spp., Neisseria meningitidis, Escherichia coli, Francisella tularensis, Klebsiella spp., Yersinia spp., Brucella spp., Shigella spp., Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae.
Use of Streptomycin is effective at treatment of an endocarditis which causes Enterococcus faecalis or Streptococcus of the viridans group (in a combination therapy with Vancomycinum or penicillin).
Streptomycin according to the instruction does not show activity concerning anaerobic bacteria of Rickettsia spp., Spirochaetaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus spp.
Release form
Streptomycin is produced in the form of porous white powder for preparation of solution for intramuscular introduction on 250 mg, 500 mg and 1 g.
The closest analog of Streptomycin is the drug Pasomycinum.
Indications to Streptomycin use
According to the instruction Streptomycin is appointed at treatment:
- Endocarditis (in a combination with ampicillin);
- Tuberculosis of various localization, including tubercular meningitis;
- Tularemias;
- Venereal granuloma;
- Brucellosis;
- Intestinal infections, and also infections of urinary tract (in cases of sensitivity of the activator);
- Plagues.
Contraindications
Use of Streptomycin is contraindicated in the following cases:
- At hypersensitivity to active component of drug, and also to aminoglycosides in the anamnesis;
- At organic lesions of the VIII couple of cranial nerves;
- In cases if the disease develops against the background of a serious chronic illness of kidneys with an azotemia and uraemia;
- At pregnancy, except cases in which the advantage of use of Streptomycin justifies possible risk.
Streptomycin according to the instruction is appointed with care:
- At a myasthenia;
- At parkinsonism;
- At a disease of botulism (to avoid disturbances of neuromuscular transmission and further weakening of skeletal muscles);
- In the period of a lactation;
- At chronic heart failure, especially II-III severity;
- At an obliterating endarteritis;
- Dehydrations;
- At disturbance of cerebral circulation;
- At children's and advanced age;
- At a chronic renal failure;
- At tendency to bleeding.
Streptomycin route of administration
The antibiotic Streptomycin is applied intratrakhealno, intramusculary, in the form of aerosols, and also inside (in cases of treatment of infections of digestive tract).
At intramuscular introduction Streptomycin appoint in a daily dosage 1-2 g, and in cases of bad portability, weighing up to 50 kg and to elderly people – on 750 mg.
The daily dosage to children is calculated proceeding from body weight:
- Up to 3 months – on 10 mg/kg;
- 3-6 months – on 15 mg/kg;
- From 6 months to 2 years – on 20 mg/kg;
- From 2 to 13 years – on 15-20 mg/kg.
At treatment of not tubercular etiology Streptomycin is entered to four times a day. Streptomycin use duration – 7-10 days.
The daily dose of drug at treatment of tuberculosis should be entered in one step, but at bad portability Streptomycin use twice a day is allowed. Treatment duration – of three months.
By Intratrakhealno an antibiotic Streptomycin three times a week on 0,5-1 g appoint no more than three weekly. If the disease develops against the background of supertension and coronary heart disease, the initial dose is reduced to 250 mg a day, however at good tolerance it can be increased.
The therapy modes Streptomycin at a renal failure adjust depending on its expressiveness.
Side effects of Streptomycin
In certain cases at use of an antibiotic of Streptomycin there can be frustration of the alimentary system in the form of abnormal liver functions, vomiting, nausea and diarrhea.
Frustration from a nervous system are most often shown as:
- Headache;
- Peripheral neuritis;
- Drowsiness;
- Neuromuscular blockade – a night apnoea, difficulty or an apnoea (most often at introduction along with muscle relaxants);
- Weakness;
- Neurotoxic action in the form of twitching of muscles and epileptic seizures;
- Neuritis of a facial nerve in the form of paresthesias, burning sensation in a face or an oral cavity.
Besides, at use of Streptomycin can develop:
- Ototoxicity – a ring, decrease or a hearing loss (in rare instances – to irreversible deafness);
- Allergic reactions – a dermahemia, an itch, rash, fever, a Quincke's disease;
- Nephrotoxicity – a polyuria, nausea, a loss of appetite, an oliguria, thirst, vomiting. The probability of development of nephrotoxicity from use of Streptomycin increases at long administration of drug in high doses, and also at renal failures;
- Local reactions in the form of a hyperemia or pain in an injection site;
- Vestibular and labyrinth disturbances – dizziness, instability, a diskoordination.
At overdose toxic reactions in the form of thirst, dizziness, vomiting, a hearing loss, a loss of appetite, disturbance of breath, an ataxy, frustration of an urination, nausea arise Streptomycin.
At use of an antibiotic Streptomycin should be considered:
- Drug is incompatible with other ototoksichny and nefrotokschny medicines, including aminoglycosides and polymyxins;
- Streptomycin can reduce efficiency of therapy by anti-myasthenic drugs;
- Neuromuscular blockade is strengthened by the narcotic analgetics, galogensoderzhashchy hydrocarbons and other drugs blocking neuromuscular transmission;
- Indometacin (at intravenous administration) reduces renal clearance of Streptomycin;
- The risk of development of undesirable effects increases at simultaneous use with metoksiflurany.
Storage conditions
Streptomycin belongs to a number of antibacterial drugs of a prescription issue with a period of storage three years.
Except people, only one living being on the planet Earth – dogs suffers from prostatitis. Here really our most loyal friends.
Statistically, can only one of ten of our compatriots brag of a decent condition of an oral cavity. On среднестатистич...
Section: Articles about health
Life expectancy in various regions of Earth is not identical. Social stability, economic wellbeing, availability and level of medical care, household comfort, literacy of the population in the field of observance sanitary гигиен exert impact on it...
Section: Articles about health
It would seem, about it there can be no disagreements: water is necessary for a human body for normal life activity, and about how and when it should be drunk, all know. It turned out that the situation is not absolutely so: for many years there are very persistent delusions connected with this question. Let's consider the most widespread of them....
Section: Articles about health
Condition of lips (their morbidity, outward) – one of indicators of health of the person. Peeling, dryness, pallor, and also трещ...
Section: Articles about health
The pine is one of the most widespread plants of our woods. Its needles and pitch not without reason called by "gallipot" were since ancient times used for strengthening of protective forces of an organism, treatment of avitaminosis, anemia and many other diseases. In recent years wide п...
Section: Articles about health
Cystitis, or inflammation of a mucous membrane of a bladder, this very widespread disease which, owing to some features of a structure of bodies of urinogenital system, women have approximately four times more often than men. Women aged from 20 up to 45 years enter into the main risk group. Cystitis is an illness of a bacterial origin. It can have an acute or chronic current. The second option is dangerous not only a frequent recurrence, серьезн...
Section: Articles about health
About 10-15 years ago existence of the computer in the apartment of the Russian was considered as a rarity and office rooms were only on перв...
Section: Articles about health
Iodine - one of thirty most important microelements in our organism. The main role of iodine consists in synthesis of thyroid hormones of a thyroid gland - the substances which are responsible for the majority of exchange processes of an organism. It is known that thyroid hormones consist...
Section: Articles about health
There comes the season of issues. Many Russians already dream of outdoor recreation, trips, beautiful seaside beaches. At this time there is no wish to think of problems with health and other unpleasant things, however there are subjects which require attention. In the summer repeatedly the risk increases to ache with some very dangerous illnesses, we also will talk about them today....
Section: Articles about health
There is a lot of fans of beer in our country. Statistically, on each average Russian (including women and children) in...
Section: Articles about health
Cellulitis - very widespread cosmetic shortcoming which arises approximately at 80% of women sooner or later. Emergence it is connected with change of structure of a hypodermic fatty layer. At the same time on the surface of skin at first there are roughnesses (cambers...
Section: Articles about health
Some people consider what for medicine of the 21st century of secrets in the field of health of the person almost does not exist. It absolutely not so. The more answers scientists receive, the more the most difficult questions are raised for them by life. Besides, there are diseases which are not explained with science in any way of which existence people know for 100-150 years. These diseases meet not so often, but from some of them nobody is insured....
Section: Articles about health
You are office worker, the driver, the fan of winter sports or do not think of life without bicycle? You conduct a slow-moving image жизн...
Section: Articles about health
It is known that the person for 80% consists of water which participates in all processes of an organism. The person loses liquid daily – as a result of sweating, breath, an urination, and its insufficient completion due to various reasons can bring to обезвожив...
Section: Articles about health
Not everyone can brag of the shining Hollywood smile. Even the person who is regularly visiting the stomatologist and watching of oral cavities over health periodically has problems: enamel of teeth darkens under the influence of some products, on it the deposits giving to teeth a grayish or yellowish shade collect....
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – one of the most vulnerable areas on a face therefore age changes concern them first of all. Whether it is possible to keep a pier...
Section: Articles about health
Color of plants is caused by presence at them of certain chemical compounds. Let's talk about what is meant by various colors of vegetables and fruit and what properties they give them....
Section: Articles about health
What will only not be thought up by persons interested to have a beautiful figure. Here the last innovation – for weight loss needs to be eaten greasy food. Let's understand whether there is at a fatty diet common sense....
Section: Slideshow
Dark circles (bruises) under eyes – a shortcoming with most of which often fight against the help of cosmetics (proofreaders, salons...
Section: Articles about health
Deciding to get rid of an addiction, not all imagine what effects it is necessary to face. Process of refusal of smoking causes quite essential discomfort in most of people: differences of mood, sleep disorder, fatigue, decrease физич...
Section: Articles about health
It would seem, to buy drugs in Moscow does not make a problem – a drugstore, and not one, is available for each resident of the capital within walking distance. And, nevertheless, Internet drugstores become more popular – what it is possible to explain such phenomenon with? Actually there is a lot of reasons and if to formulate them it is short, then the most suitable word will be - "conveniently". We suggest to get acquainted in more detail with pluses and minuses of online drugstores that buying drugs, not to make the wrong choice....
Section: Articles about health
The problem of diagnosis was and remains to one of the most important in medicine. From that, the reason недо will be how precisely defined...
Section: Articles about health
Small appetite at the child – the complaint which pediatricians should hear practically from each mother. Most often it is carried to the category of children's whims, however the refusal of food in certain cases can be to alarming symptoms therefore it cannot be ignored....
Section: Articles about health
Many parents of children at the age of 2-4 years face excessively whimsical behavior of the child. The kid exhausts constant crying and whims not only the parents, but also himself. In what the reasons of children's whims. And how to fight with them?...
Section: Slideshow
The business lady, the become mother, it is necessary to solve an array of problems. But of them is main: how to combine the beloved child and work?...
Section: Slideshow
Hemorrhoids – extremely widespread disease. Periodically arising inflammations and bleeding of hemorrhoidal nodes cause serious discomfort to nearly fifteen percent of adults. Meanwhile, having a clear idea of the aggravation reasons...
Section: Articles about health
The unpleasant feelings connected with spring breakdown are familiar almost to each of us. Often happens that in March-April on the person weakness leans: he suffers from drowsiness, complains of bad mood, loss of interest in life and failures in affairs....
Section: Articles about health