





Thiamin
Application instruction:
Thiamin is a water-soluble B1 vitamin which is applied to completion of its deficit in an organism, and also to treatment of a number of diseases.
Pharmacological effect of Thiamin
In an organism Thiamin turns into a coenzyme cocarboxylase. It is a part of many enzymes catalyzing biochemical reactions. By means of cocarboxylase vitamin plays an important role in carbohydrate, proteinaceous and a lipometabolism. Regulating thus a metabolism, it exerts positive impact on all organism at different pathological processes.
Feature of Thiamin is its ability to influence carrying out nervous excitement in synapses, improving it. It is possible because of change of polarization of membranes in neuromuscular connection thanks to what moderate ganglioblokiruyushchy effect is had. B1 vitamin is also capable to protect cells from destruction by oxygen radicals, that is shows antioxidant properties.
Drug after hit in blood widely spreads in fabrics, its about a half gets into muscles. Removal is carried out with a stake and urine. As vitamin water-soluble, it is not capable to collect in an organism and is quickly removed.
Release form
Thiamin according to the instruction is produced in the form of solution for injections, capsules and tablets.
Indications to Thiamin use
Thiamin according to the instruction is applied to completion in an organism of its deficit at the increased need for it, insufficient receipt or excess loss, and also to treatment of some diseases.
Insufficient content of Thiamin is called B1 hypovitaminosis, and its total absence – B1 avitaminosis (a beriberi disease).
Drug is included into schemes of treatment of diseases of a nervous system - neuritis, polyneurites, radiculitises, peripheral paresis and paralyzes, neuralgia.
In dermatology B1 vitamin is applied at a neurogenic dermatosis, a skin itch, pyodermas, psoriasis, eczema.
Thiamin received good comments in complex treatment of diseases of the alimentary system – a peptic ulcer of a stomach and a duodenum, an atony of intestines, liver diseases.
At a long physical and mental overstrain, during pregnancy and feeding by a breast, at patients on a hemodialysis the need for B1 vitamin sharply increases, and demands completion from the outside.
Contraindications
Thiamin according to the instruction is not appointed at its intolerance if it was registered earlier.
Application instruction of Thiamin
Ways of administration of drug different – inside and parenterally (intramusculary, subcutaneously, intravenously).
For intake in the form of Thiamini chloridum the adult dosage makes 10 mg of 1 - 3 time a day, to children 3 years – on 5 mg every other day, aged from 3 up to 8 years – on 5 mg 3 times a day in a day, a course of 30 days are younger.
In need of more bystry saturation of an organism as Thiamin choose a parenteral way of introduction. The drug is administered 1 time a day, the adult on 1 ml, children on 0,5 ml, the course makes from 10 to 30 injections. Because of a low rn parenteral injections are painful.
It is impossible to enter at the same time parenterally B1, B6 and B12 vitamins – it will reduce their medicinal action and will increase probability of allergic reaction. Use of Thiamin and niacin in one syringe is impossible.
Side effects
According to reviews Thiamin is well transferred, but is sometimes capable to cause allergic reactions in the form of a small tortoiseshell, a Quincke's edema, a skin itch, is very rare – an acute anaphylaxis. At parenteral administration of reaction are stronger, than at intake. Also perspiration and increase of heartbeat meet.
In operating time our brain spends the amount of energy equal to the 10 Watts bulb. So the image of a bulb over the head at the time of emergence of an interesting thought is not so far from the truth.

We live during an advertizing era. Daily each person receives a solid portion of persuasive councils about what to eat to be здо...
Section: Articles about health
For the last decades the diabetes mellitus of the second type became really world problem. The number of cases annually increases, and average age of patients for whom the illness is diagnosed, steadily decreases. Specialists consider that one of osno...
Section: Articles about health
Antibiotics - - it is possible to call the chemical compounds suppressing growth of bacteria the break in the field of medicine which allowed to save mankind from many diseases incurable earlier: tuberculosis, plague, syphilis and many others. The contribution of drugs to rescue of people from epidemics of dangerous infections is huge, however at careless use antibiotics are capable to cause to an organism serious damage. Negative action can be shown in the form of easing of immunity, disturbance of balance of microflora in кишеч...
Section: Articles about health
The modern person not always manages to find housing in the environmentally friendly region and such work which would not do harm здо...
Section: Articles about health
The mankind knows that some toxins at intake in the minimum quantities have therapeutic effect from an extreme antiquity. Many substances recognized poisonous are applied in the medical purposes also today, being the main deystvuyushch...
Section: Articles about health
All diseases from nerves – in this joke a big element of truth, are said by doctors. Constant stresses lead to decrease in protective forces of an organism, and it becomes vulnerable for a set of diseases. It is wrong to think that the stress is a problem of the present. Life of people and hundred, and one thousand years ago also abounded with problems therefore need of a relaxation understood in ancient times – to some techniques more than one thousand years. The person needs knowledge of how it is possible to relax, this knowledge пригод...
Section: Articles about health
Shops of household appliances offer us the huge choice of various devices for the house. Whether there are among this abundance devices which...
Section: Articles about health
Frosty air, fresh wind and easy snowball at most of Russians are associated with cheerfulness, health and cheerful entertainments on which our winter is so generous. But, unfortunately, cold season sometimes brings also troubles with health. It is not about a season...
Section: Articles about health
A little more than a century ago goat milk was a traditional food stuff of most of Russians. Unfortunately, today on tables of our compatriots it appears extremely seldom. The reason that the use of so useful product practically came to naught, not only in very modest volumes of its production and, respectively, rather high cost. Potential consumers are just insufficiently informed on unique properties of goat milk and that advantage which...
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – one of the most vulnerable areas on a face therefore age changes concern them first of all. Whether it is possible to keep a pier...
Section: Articles about health
Vitamin complexes belong to the most popular drugs, probably, in our country there is no person who was not hearing about advantage of vitamins and never their accepting. The more vitamins, the better, we consider and as it appeared, cruelly we are mistaken. So l...
Section: Articles about health
Venereal diseases in medicine are called the infections which are transmitted preferential sexually, now they and are called - infections, sexually transmitted, or STD. Among them is also life-threatening. In spite of the fact that the majority of diseases such will respond to treatment, they are widespread everywhere, and there is no tendency to decrease in incidence. Besides, some of them promptly look younger: statistically, a third of young people at the age of 16-22 years of a str...
Section: Articles about health
People know that thermal sources have salutary force long ago. Treatment by natural waters is one and...
Section: Articles about health
Memory is an ability of the central nervous system to fix, keep and as necessary to reproduce information on knowledge or skills received by the person or an animal during life. The mechanism of this process is up to the end not studied....
Section: Articles about health
Some people consider what for medicine of the 21st century of secrets in the field of health of the person almost does not exist. It absolutely not so. The more answers scientists receive, the more the most difficult questions are raised for them by life. Besides, there are diseases which are not explained with science in any way of which existence people know for 100-150 years. These diseases meet not so often, but from some of them nobody is insured....
Section: Articles about health
The business lady, the become mother, it is necessary to solve an array of problems. But of them is main: how to combine the beloved child and work?...
Section: Slideshow
Partial and the more so full loss of hearing significantly reduces quality of life. Difficulties with communication lead to loneliness and isolation. The person who badly hears experiences difficulties with social and professional implementation, quite often has problems in...
Section: Articles about health
Diapers for adults – individual one-time means of hygiene which in some situations is irreplaceable and from such situations any person is not insured. Though nobody perceives need of their use with enthusiasm, however without such means already problematic situation could be heavier....
Section: Articles about health
Smack in a mouth can arise in the natural way – as a result of lack of morning hygiene or reception of the corresponding food. Odn...
Section: Articles about health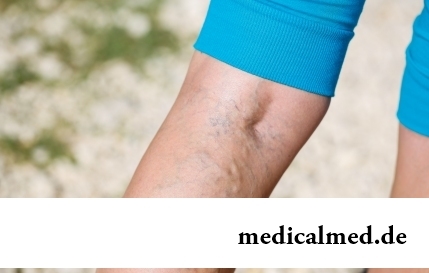
The varicosity has familiarly many, statistically, this disease more than a half of all adult population. As a rule, the varicosis affects preferential superficial vessels, and is shown by characteristic cosmetic defects. Guo...
Section: Articles about health
The unpleasant feelings connected with spring breakdown are familiar almost to each of us. Often happens that in March-April on the person weakness leans: he suffers from drowsiness, complains of bad mood, loss of interest in life and failures in affairs....
Section: Articles about health
Condition of lips (their morbidity, outward) – one of indicators of health of the person. Peeling, dryness, pallor, and also трещ...
Section: Articles about health
Food with the increased content of sugar is attractive to most of people - it is scientifically confirmed fact. Business here not in intemperance or dissoluteness: the sweet food is associated since childhood with feeling of rest and safety which is felt by the kid, to...
Section: Articles about health
Reactive pancreatitis - the disease which is characterized by inflammatory process in a pancreas which arises most often because of excess activity of digestive enzymes. It − the emergency state which treatment has to take place in surgical department under control of doctors. The acute inflammation of gland can become the reason of its transition to a chronic form, and also development is purulent - necrotic pancreatitis which the extensive necrosis of fabrics can follow. Zabolev...
Section: Articles about health
Not without reason doctors say that 90% of diseases begin or develop because of misoperation of intestines. Disturbance of its functions связ...
Section: Articles about health
One of the major chemical processes happening in a human body are oxidation reactions. They go with participation of fats and carbohydrates which we receive from food, and the oxygen getting to us from air. A main goal of such reactions is it is received...
Section: Articles about health
Let's begin with the fact that a separate illness which is called "adjournment of salts", just does not exist. In practice this household name of disbolism leading to development of a number of diseases. Pathological process consists that in an organism there is an accumulation of salts of uric acid (as a rule, owing to failure of a water salt metabolism or insufficiently effective work of secretory system)....
Section: Articles about health
