Intracranial hematoma
The intracranial hematoma (blood tumor) represents accumulation of blood in a head cavity which reduces 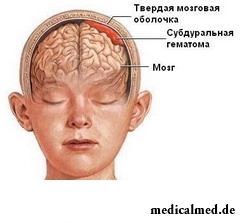 intracranial space and promotes a brain prelum. There are similar accumulations of blood as a result of a rupture of aneurism, injuries of vessels and hemorrhages – in a tumor, an infectious origin or as a result of a stroke.
intracranial space and promotes a brain prelum. There are similar accumulations of blood as a result of a rupture of aneurism, injuries of vessels and hemorrhages – in a tumor, an infectious origin or as a result of a stroke.
Feature of an intracranial hematoma is that clinical manifestations arise not at once, and later some period.
The most important danger of an intracranial hematoma consists that she puts the essential pressure upon a brain. As a result wet brain with defeat of brain fabric and its subsequent destruction can be formed.
Types of intracranial hematomas
Hematomas happen:
- acute – symptoms are shown for 3 days from the moment of education;
- subacute – symptoms are shown for 21 days;
- chronic – manifestation of symptoms occurs after 21 days from the moment of education.
By the sizes distinguish small hematomas (to 50 ml), averages (50-100 ml) and big (it is more than 100 ml).
In the place of localization of a hematoma subdivide on:
- epidural, being over a firm cover of a brain;
- subdural, with localization between substance of a brain and its firm cover;
- intracerebral and intra ventricular which place of localization is the share directly of brain substance;
- intracranial hematomas of a trunk of a brain;
- the diapedetic hematomas resulting from hemorrhagic treatment, at the same time integrity of vessels it is not broken.
Main reasons for developing of an intracranial hematoma
The disease or injury is the main reason for an intracranial hematoma.
So, subdural hemorrhage often results from a rupture of the veins connecting a brain and venous system, and also sine of a firm cover of a brain. The hematoma which squeezes brain tissues is as a result formed. As blood from a vein collects slowly, symptoms of a subdural hematoma can not be shown for several weeks.
The epidural hematoma is usually formed as a result of a rupture of an artery or a vessel between a skull and an external surface of a firm cover of a brain. In arteries pressure of blood is higher, than in veins therefore blood follows from them quicker. The epidural hematoma quickly increases in sizes and strengthens pressure upon brain fabric. Symptoms are usually shown quickly enough, sometimes even within several hours.
The intracerebral hematoma is formed as a result of penetration into a blood brain. If the hematencephalon results from getting injured, then white matter of a brain preferential is surprised. Such damage is resulted by a rupture of neurites which cease to transfer impulses in different parts of a body. The intracerebral hematoma can be formed also as a result of a hemorrhagic stroke. In this case hemorrhage comes from unevenly thinned wall of an artery and blood under high pressure gets to tissues of a brain and fills free space. Such hematoma can be formed on any site of a brain.
Thinning and ruptures of vessels result, as a rule, from tumors, infections, angioneurotic disturbances, atherosclerotic defeats, etc.
There can sometimes be diapedetic hemorrhages resulting from a hyperpermeability of vessels (at change of coagulant properties of blood or a fabric hypoxia). It leads to formation of accumulations of blood around the damaged vessels which often combine, and the intracranial hematoma is formed.
Symptoms of an intracranial hematoma
Often symptoms of an intracranial hematoma are shown later a certain period. The main symptoms depend on the nature of an intracranial hematoma and its size. As the hematoma preferential develops as a result of traumatic damage, and symptoms generally prevail, characteristic of injury of a brain. Besides, the symptomatology of a hematoma can differ depending on age of the patient.
At an epidural 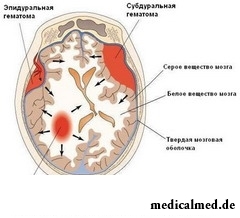 hematoma symptoms are shown quickly. Patients are tormented by a severe headache, drowsiness, confusion of consciousness. Often patients with an epidural hematoma fall into coma. At formation of a hematoma more than 150 ml of people dies. The progressive mydriasis on the party of a hematoma is noted. To the patient there can be epileptic seizures, paralyzes and the progressing paresis. At children symptoms of an epidural hematoma have the following character: there is no primary loss of consciousness, hypostasis develops very quickly and demands immediate operational treatment of an intracranial hematoma.
hematoma symptoms are shown quickly. Patients are tormented by a severe headache, drowsiness, confusion of consciousness. Often patients with an epidural hematoma fall into coma. At formation of a hematoma more than 150 ml of people dies. The progressive mydriasis on the party of a hematoma is noted. To the patient there can be epileptic seizures, paralyzes and the progressing paresis. At children symptoms of an epidural hematoma have the following character: there is no primary loss of consciousness, hypostasis develops very quickly and demands immediate operational treatment of an intracranial hematoma.
At formation of a subdural hematoma symptoms, as a rule, are not shown at once, and initial defeat seems insignificant. Usually symptoms begin to be shown several weeks later. At small children increase in the head in sizes can be observed. At patients of old age the subacute course of a hematoma is observed. Young patients feel a headache, in the subsequent vomiting and nausea, epileptic seizures and spasms can develop. The mydriasis from damage can be noted, but not always. Small intracranial hematomas can independently resolve, and big hematomas need emptying.
At an intracerebral hematoma as a result of a hemorrhagic stroke the symptomatology depends on the defeat center. The most frequent symptoms are a headache (preferential on the one hand), hoarse breath, a loss of consciousness, and also paralysis, spasms and vomiting. At defeat of a brainstem treatment of an intracranial hematoma is impossible, and the patient dies.
At an intracranial hematoma which was formed owing to an extensive injury, symptoms, as a rule, such: headache, loss of consciousness, vomiting, nausea, epileptic seizures, spasms. It is usually possible to define localization of such hematoma only as a result of an operative measure.
At formation of a hematoma owing to a rupture of aneurism the main symptom is acute and sharp pain in the head (as blow of a dagger).
Treatment of an intracranial hematoma
Preferential treatment of an intracranial hematoma assumes an operative measure. The type of operation often depends on the nature of a hematoma.
After carrying out operation the doctor appoints anticonvulsant medicines for prevention or control of posttraumatic spasms. Sometimes, that similar spasms begin at the patient even a year later after getting injured. For some time at the patient amnesia, a headache and disturbance of attention is possible.
The recovery period after an intracranial hematoma usually very long. The period of recovery takes, at least, half a year adult patients. Children are, as a rule, recovered much quicker.
Blood of the person "runs" on vessels under huge pressure and at disturbance of their integrity is capable to shoot of distance to 10 meters.
Zone hypostases under eyes - very widespread problem giving to people is a lot of inconvenience. Hypodermic fabric in these parts having...
Section: Articles about health
Heart disease and blood vessels lead to disturbance of blood supply of bodies and fabrics that involves failures in their work, deterioration in health of the person, decrease in its working capacity and standard of living. Annually such perishes from pathologies more...
Section: Articles about health
It would seem, to buy drugs in Moscow does not make a problem – a drugstore, and not one, is available for each resident of the capital within walking distance. And, nevertheless, Internet drugstores become more popular – what it is possible to explain such phenomenon with? Actually there is a lot of reasons and if to formulate them it is short, then the most suitable word will be - "conveniently". We suggest to get acquainted in more detail with pluses and minuses of online drugstores that buying drugs, not to make the wrong choice....
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – one of the most vulnerable areas on a face therefore age changes concern them first of all. Whether it is possible to keep a pier...
Section: Articles about health
All the known slogan "Protect Men!" arose not from scratch. In a sense, the nature created men much less adapted for vital disorders, than it seems at first sight. Statistically, men are ill more often...
Section: Articles about health
In consciousness of our many compatriots idea that folk remedies if are no more effective, than medicinal "chemistry" strongly took roots, then are precisely less harmful. Unfortunately, it is not always fair: some methods of treatment consecrated with "century national experience" can work so on the patient that it will need urgent intervention of physicians....
Section: Articles about health
They say that to ensure health and longevity of people it is obliged. Really, at competent approach to these questions, we will pass...
Section: Articles about health
Color of plants is caused by presence at them of certain chemical compounds. Let's talk about what is meant by various colors of vegetables and fruit and what properties they give them....
Section: Articles about health
Turnip, radish, horse-radish – once these and other products enjoyed wide popularity at our ancestors, being not only the food sating an organism but also the medicines curing of many diseases. Unfortunately, the use of some of them got out of fashion long ago, and once favourite plants and vegetables almost ceased to make a contribution to human health. Inclusion of such products in a modern diet − an effective measure of prevention and treatment of diseases which seldom suffered...
Section: Articles about health
Feeding by a breast - the integral part of ideal motherhood allowing to come into contact with the kid and to create since early years...
Section: Articles about health
About 10-15 years ago existence of the computer in the apartment of the Russian was considered as a rarity and office rooms were only at the first stage of equipment by these useful devices. Today practically in each house there is a computer (and often not one), and to constants...
Section: Articles about health
The majority of gynecologic diseases prove three main signs, each of which speaks about need of a visit to the gynecologist. Certainly, it is possible to establish the exact diagnosis only after inspection, but on the basis of some signs it is possible to assume existence of this or that pathology. Let's consider symptoms of the female diseases which are found most often....
Section: Articles about health
Since the moment when the child becomes a school student, his sight begins to be exposed to the strengthened loadings which are supplemented viewing...
Section: Articles about health
The words "disease" and "patient" not without reason come from one root – "pain". As a rule, symptoms of illnesses thoroughly spoil to patients life. However from this rule there are exceptions. Some diseases are shown by signs which can cause even полож...
Section: Articles about health
Dietary supplements (dietary supplements) for the last decades were so thoroughly included into our life that, apparently, it is already impossible to find the person who at least once did not try them. At the same time, most of our compatriots have a vague idea of what dietary supplements as they affect a human body consist of and what differ from the real medicines in. Let's try to understand these questions, and at the same time and to understand, such additives are how necessary for us....
Section: Articles about health
Life activity of one-celled fungi of the sort Candida is a proximate cause of development of candidiasis (milkwoman), it is related...
Section: Articles about health
It is known that the person for 80% consists of water which participates in all processes of an organism. The person loses liquid daily – as a result of sweating, breath, an urination, and its insufficient completion due to various reasons can bring to обезвожив...
Section: Articles about health
No, probably, the person who would not have cold. Cold, cough, a headache – these symptoms are known to everyone. The peak of catarrhal diseases is the share of fall. SARS already came to schools and kindergartens, flu slowly makes the way to the cities, in a word, winter close!...
Section: Articles about health
The endocrine system carries out in a human body extremely important role, practically all processes of life activity регулируютс...
Section: Articles about health
Let's begin with the fact that a separate illness which is called "adjournment of salts", just does not exist. In practice this household name of disbolism leading to development of a number of diseases. Pathological process consists that in an organism проис...
Section: Articles about health
Cold is such painful that each sigh becomes a victory, heat "knocks" down, and the ache in joints forces to think only of pain. Some people with approach of the first symptoms of cold make the self-sacrificing decision to have a disease standing, and at best to rest in bed with a cup of hot tea. There is an opinion that if not to treat cold, then the organism itself, sooner or later, will overcome an illness. Whether so it? It is known that if in time it is simple not to begin treatment, apparently, harmless...
Section: Articles about health
It is impossible to imagine human life in which there would be no plants. Practically in each apartment and any of productions...
Section: Articles about health
Some people consider what for medicine of the 21st century of secrets in the field of health of the person almost does not exist. It absolutely not so. The more answers scientists receive, the more the most difficult questions are raised for them by life. Besides, there are diseases, not объясн in any way...
Section: Articles about health
Diseases of joints often begin imperceptibly for the person. The first stages of destruction of the cartilaginous tissue providing soft and free sliding of heads of bones in joint bags proceed slowly and absolutely without serious consequences. Especially unpleasantly for the fact that this process is not connected with advanced age: degradation of joint surfaces is, as a rule, noticeable after 30 years. It means that practically each able-bodied person at any time can face sad results...
Section: Articles about health
The Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) are plants or animals (as a rule, agricultural) in whose genotype...
Section: Articles about health
What woman does not dream of a beautiful and thick hair? While physicians developed difficult schemes on hair transplant, in the industry of hairdresser's art a few years ago there was a sensation – methods of hair extension appeared. It would seem, dreams came true...
Section: Articles about health
Each of us repeatedly noticed that the people having the same passport age are sometimes not similar on one-years at all. One at the age of 40-45 years already looks almost an old man, and another and in 60 is young, vigorous and full of life. The matter is that the condition of our health depends not on the number of the lived years, and on degree of safety of an organism. This factor also defines biological age of the person....
Section: Articles about health